A ball mill is a mechanical device used to grind materials into fine powder. It is extensively utilized in various industries, including mining, construction, and chemistry. This essay will explore the purpose and applications of a ball mill, highlighting its key functions and advantages.
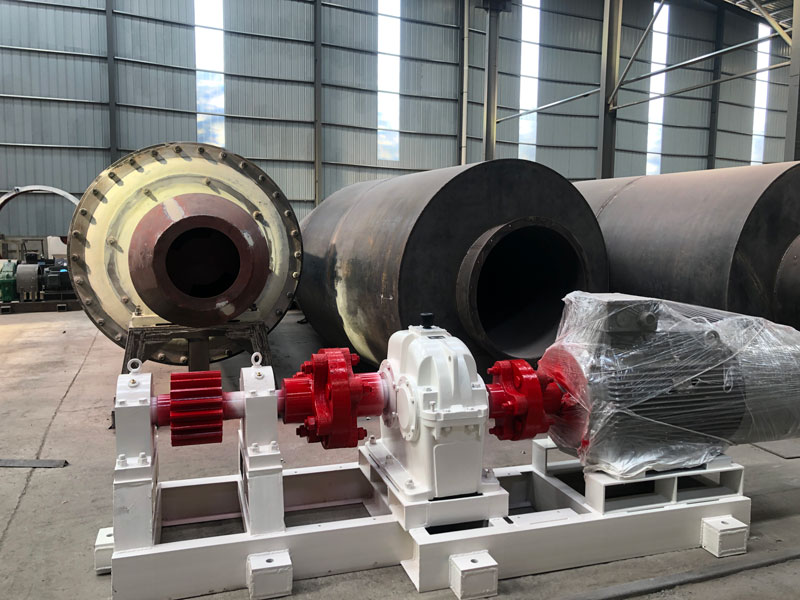

I. Definition and Components
A. Definition of a Ball Mill:
1. Briefly explain that a ball mill is a cylindrical machine designed for grinding materials.
2. Mention that it consists of a rotating drum filled with grinding media, such as balls or rods.
B. Main Components:
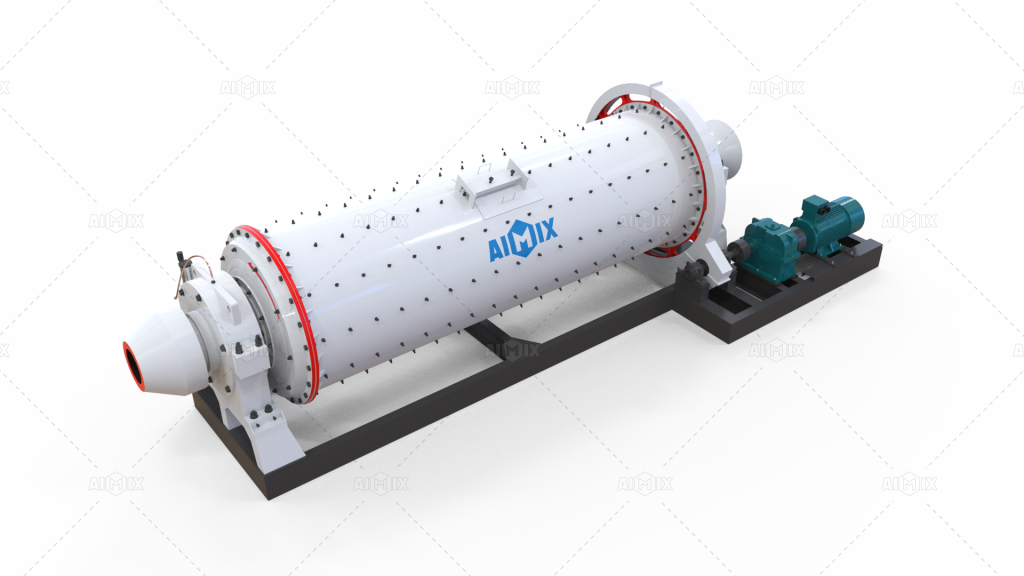
1. Describe the cylindrical shell of the ball mill, typically made of steel, which houses the grinding media.
2. Highlight the motor, which rotates the drum, and the gearbox responsible for maintaining the desired rotational speed.
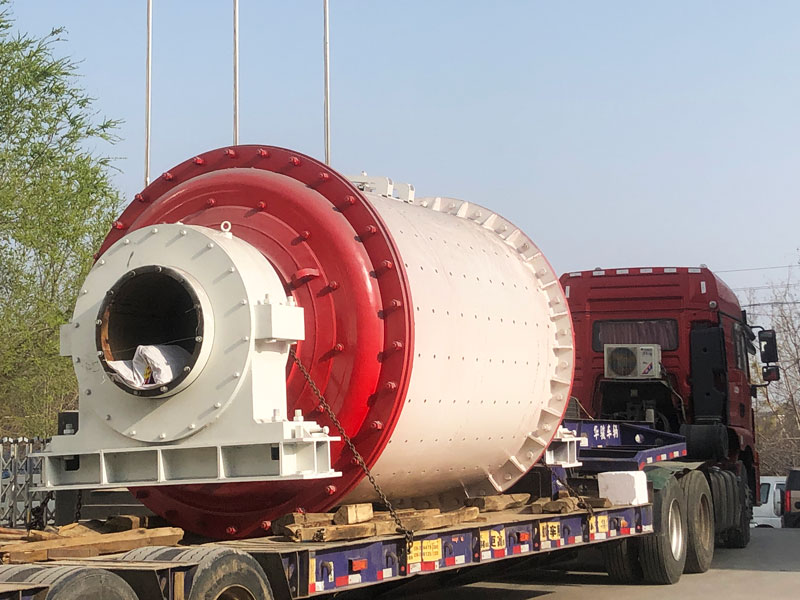

II. Grinding Process
A. Principles of Grinding:
1. Explain that the primary purpose of a ball mill is to reduce the size of materials through grinding.
2. Discuss how the grinding media inside the mill collide with the material, resulting in particle size reduction.
B. Types of Grinding Mechanisms:
1. Mention impact grinding, where the grinding media strike the material and break it into smaller particles.
2. Discuss attrition grinding, where the grinding media rub against the material, wearing it down gradually.
III. Applications of Ball Mills
A. Ore Grinding in Mining Industry:
1. Elaborate on the crucial role of ball mills in ore processing, where they crush and grind the mined ore into fine particles.
2. Highlight their usage in extracting valuable minerals from ores, such as gold, copper, and iron.
B. Cement Production:
1. Explain how ball mills are essential in the cement manufacturing process, where they pulverize clinker, gypsum, and other additives to produce cement.
2. Discuss the importance of controlling particle size distribution in cement production for optimal material properties.
C. Chemical Industry:
1. Mention the utilization of ball mills in chemical processes, including grinding and blending of raw materials.
2. Describe their role in preparing chemical compounds and catalysts, enhancing reaction rates and efficiency.
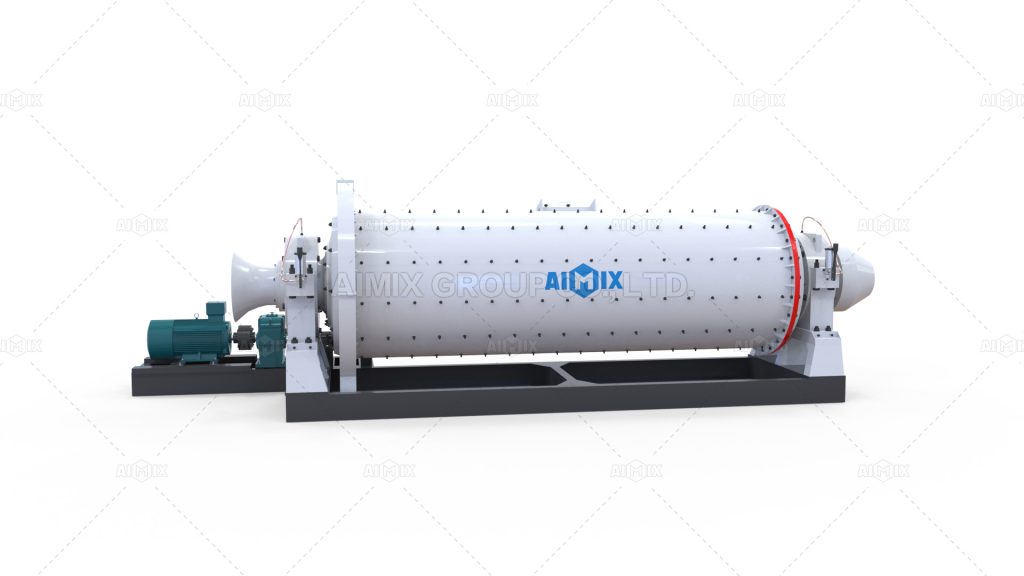

IV. Advantages of Ball Mills
A. Versatility and Flexibility:
1. Highlight that ball mills can grind a wide range of materials, from soft to hard, brittle to ductile.
2. Discuss how the mill’s design allows for different grinding modes, such as wet or dry grinding.
B. Efficient Size Reduction:
1. Emphasize the high efficiency of ball mills in reducing particle size due to the impact and attrition mechanisms.
2. Mention that properly designed ball mills can achieve narrow particle size distributions for specific applications.
C. Scalability and Cost-Effectiveness:
1. Explain that ball mills are available in various sizes and capacities to accommodate different production requirements.
2. Discuss how ball mills offer a cost-effective solution for grinding large quantities of material compared to alternative methods.
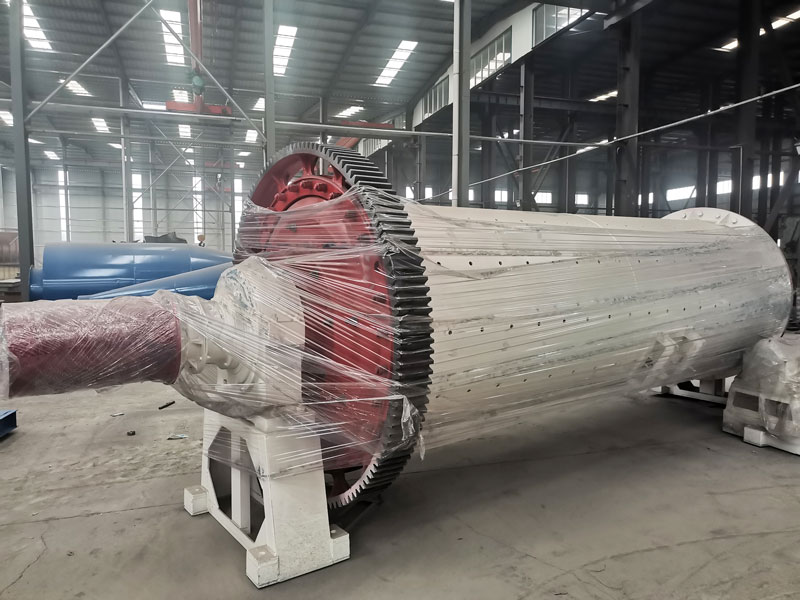

How About The Relationship Between Crusher Plants And Ball Mill
I. Complementary Functions
A. Crushing and Size Reduction:
1. Crushers: Breaking down raw materials into smaller fragments.
2. Purpose of Crushers: Preparing materials for further processing.
B. Grinding and Pulverization:
1. Ball Mills: Grinding materials into fine particles.
2. Mechanisms Involved: Impact and attrition.
II. Workflow Integration
A. Sequential Process Flow:
1. Material Flow: From crushers to ball mills.
2. Importance of Sequence: Crushing before grinding.
B. Material Handling and Conveyance:
1. Efficient Material Transfer: Conveyors, chutes, etc.
2. Smooth Transition: Between crusher plants and ball mills.
III. Interdependence in Mineral Processing
A. Ore Processing:
1. Crushers in Action: Breaking down mined ores.
2. Role of Ball Mills: Grinding ore into fine particles.
B. Circuits and Optimization:
1. Grinding Circuits: Integrating crushers and ball mills.
2. Maximizing Efficiency: Balancing crushing and grinding.
IV. Equipment Selection and Sizing
A. Compatibility and Capacity:
1. Matching Capacities: Crusher plants and ball mills.
2. Ensuring Continuous Flow: Proper equipment selection.
B. Coordinated Design Considerations:
1. Collaborative Design: Crusher plants and ball mills.
2. Optimized Performance: Layouts and workflows.

Understanding the relationship between crusher plants and ball mills is essential in mining and construction industries. Crushers prepare raw materials for processing, while ball mills grind them into fine particles. Their workflow integration, interdependence in mineral processing, and coordinated design considerations contribute to efficient operations. By aligning capacities and optimizing equipment selection, industries can achieve continuous material flow and improved performance.